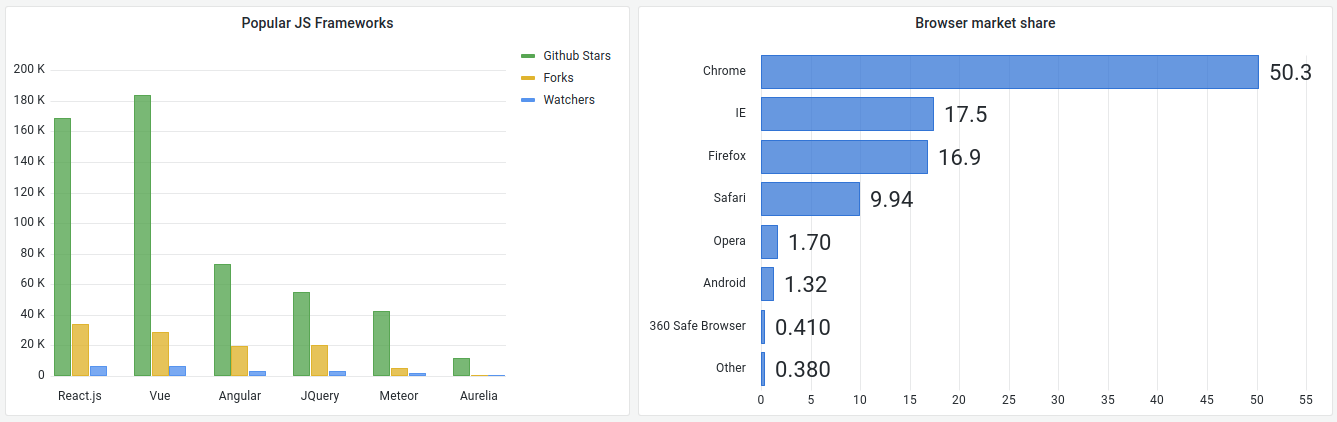
A barchart is one of the simplest ways to turn numbers into easy-to-read visuals. Whether you are looking to compare data between groups or track changes over time, a barchart makes it clear and quick to understand. Each bar in the chart represents a value, and the length of the bar shows how big or small that number is.
When making a barchart, you need data that can be put into two parts: one that tells what the data is about (like a name or time) and one that gives the number (like a total or score). The names go along one side of the chart, and the numbers are shown by the bars. It’s a great tool when you want to see patterns in the data right away.
What is a Barchart and Why is It Important?
A barchart is a simple and effective way to display data visually. It helps people understand numbers quickly by turning them into easy-to-read bars. These charts are used to compare different groups or see how things change over time. The length of each bar shows the size of the number, making it easy to see which group is bigger or smaller.
One reason why a barchart is so useful is that it makes data easy to understand at a glance. Instead of looking through a long list of numbers, people can instantly spot patterns. For example, if you are comparing sales numbers for different products, a barchart will show which product sold the most and which sold the least in a clear, visual way.
Barcharts are important because they can simplify complex information. Whether it’s for business reports, school projects, or scientific research, using a barchart helps you communicate your findings in a way that’s easy for everyone to understand.
How to Choose the Right Data for a Barchart
When creating a barchart, it’s important to select the right type of data. You need one part of your data to be a label, such as names, categories, or time, and the other part to be numbers that show quantity, like sales, scores, or totals. The labels will go on one side of the chart, and the numbers will be represented by bars of different lengths.
It’s also essential to choose data that makes sense when compared side by side. A barchart works best when you want to compare data between different groups. For example, comparing test scores of students or sales in different months are great uses of barcharts. If the data is too similar or too different, a barchart may not be the best choice.
Make sure your data is clean and clear before you create the barchart. If there are any errors in your data, the chart may give misleading information. Always double-check your numbers before turning them into a chart.
Setting Up a Barchart: What You Need to Know
Before you create a barchart, there are a few key things to set up. First, decide whether you want your bars to be horizontal or vertical. In a vertical barchart, the bars go up and down, and in a horizontal one, they go side to side. The choice depends on how long your labels are and how many groups you want to show.
Next, think about the spacing between your bars. If the bars are too close together, they can look crowded and hard to read. But if they are too far apart, it can make the chart look empty. Finding the right balance helps make your barchart look neat and easy to read.
Another important step is to label the x-axis and y-axis clearly. The x-axis will usually have the group names or categories, and the y-axis will show the numbers. Proper labeling ensures that people can understand the information in your chart without confusion.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Barcharts: Which One to Use?
Choosing between a horizontal or vertical barchart depends on your data and your audience. A vertical barchart is the most common, with bars going up and down. This works well for most types of data, especially when the categories on the x-axis are short and simple. Vertical bars are easy for people to read and understand.
A horizontal barchart is better when the labels for each category are long, or when you have many categories. Horizontal bars make it easier to fit long names or descriptions without crowding the chart. This type of chart is also useful when you want to compare many groups, as it can fit more bars on the screen.
Both types of barcharts have their strengths, and the best choice depends on the specifics of your data. Think about how your chart will look and which version will make your data easier to read.
The Best Way to Label Your Barchart for Clarity
Labeling your barchart correctly is one of the most important steps in making it clear and easy to understand. Without proper labels, viewers might be confused about what the bars represent. Always start by labeling both axes of your barchart. The x-axis usually holds the categories or names, while the y-axis shows the numbers or values.
When labeling, it’s important to avoid long labels on a vertical it because they can overlap. In this case, a horizontal barchart might be a better choice. If you must use a vertical chart, you can rotate the labels to fit them better. Clear and concise labels will make your chart easy to read and understand.
In addition to labeling the axes, you can also label each individual bar. This is especially helpful when there are many bars that are close in size. Adding the exact value at the top of each bar helps the reader see the differences more clearly.
Understanding Bar Width and Spacing in a Barchart
The width and spacing of the bars in your barchart can greatly affect how easy it is to read. If the bars are too wide or too close together, they can become difficult to distinguish. On the other hand, if they are too thin or spaced too far apart, the chart may look confusing or incomplete.
When adjusting bar width, try to find a balance that makes your chart look visually appealing without losing clarity. Usually, you want the bars to be wide enough to show the data clearly, but not so wide that they overlap or clutter the chart. The spacing between bars should also be even, giving the chart a clean and organized look.
Also, think about the total number of bars in your it. If there are too many bars in one chart, it can be hard to read. In this case, you might consider splitting your data into multiple charts or using a different type of visualization.
Should You Stack Bars in a Barchart? When and Why
Stacking bars in a barchart can be a great way to compare parts of a whole. In a stacked barchart, each bar is divided into sections, with each section representing a different category or value. This is helpful when you want to show how different groups contribute to a total.
For example, if you’re comparing sales data for different products over several months, you could use a stacked i. Eatch bar would represent total sales for a month, and the different sections of the bar would show how much each product contributed. This allows you to see both the total amount and the breakdown for each group.
However, stacked it can be harder to read than regular it, especially when there are many categories. It’s important to use clear labels and contrasting colors to make the sections stand out. Stacking should be used when you want to highlight the relationship between the parts and the whole.
Using Colors Effectively in Your Stacked Barchart
- Use different colors for each category
- Make sure colors have enough contrast
- Avoid too many similar shades that may confuse readers
Labeling Sections for Better Understanding
- Add labels for each part of the bar
- Include a legend to explain the color coding
How to Make Your Barchart More Interactive
Interactive barcharts allow users to engage with the data, making it easier to understand large datasets. Adding interactive elements like hover effects, tooltips, and clickable sections can enhance the user’s experience and make your it more engaging. When users hover over a bar, they can see detailed information about that specific value, which is especially helpful for charts with a lot of data points.
If you are presenting your barchart online or in a digital format, consider using software or tools that support interactivity. Programs like Excel, Google Sheets, or specialized data visualization tools like Grafana or Power BI offer options to create interactive charts. These tools allow you to make your chart dynamic and easy to explore.
Adding interactivity also helps when your it contains too much information to display at once. Interactive features can help viewers focus on specific parts of the chart, making the data easier to digest.
Conclusion
In summary, a barchart is a great tool for showing data in a way that’s easy to understand. It helps you see differences between groups quickly by using bars of different lengths. Whether you’re comparing numbers, looking at trends, or showing parts of a whole, a barchart makes complex information simple and clear.
Using a it can help in many areas like school projects, business reports, or even personal tasks. It’s important to choose the right data, label everything clearly, and decide whether to use horizontal or vertical bars. By following these steps, your it will be easy to read and share with others.